Group Regression Analysis and Visualization
Shixiang Wang
Central South Universitywangshx@csu.edu.cn
2026-01-18
Source:vignettes/bregr-group-by.Rmd
bregr-group-by.RmdWe are using the same example from the ezcox package vignette.
Load the package and data.
library(bregr)
#> Welcome to 'bregr' package!
#> =======================================================================
#> You are using bregr version 1.4.0
#>
#> Project home : https://github.com/WangLabCSU/bregr
#> Documentation: https://wanglabcsu.github.io/bregr/
#> Cite as : https://doi.org/10.1002/mdr2.70028
#> Wang, S., Peng, Y., Shu, C., Wang, C., Yang, Y., Zhao, Y., Cui, Y., Hu, D. and Zhou, J.-G. (2025),
#> bregr: An R Package for Streamlined Batch Processing and Visualization of Biomedical Regression Models. Med Research.
#> =======================================================================
#>
data <- survival::lung
data <- data |>
dplyr::mutate(
ph.ecog = factor(ph.ecog),
sex = ifelse(sex == 1, "Male", "Female")
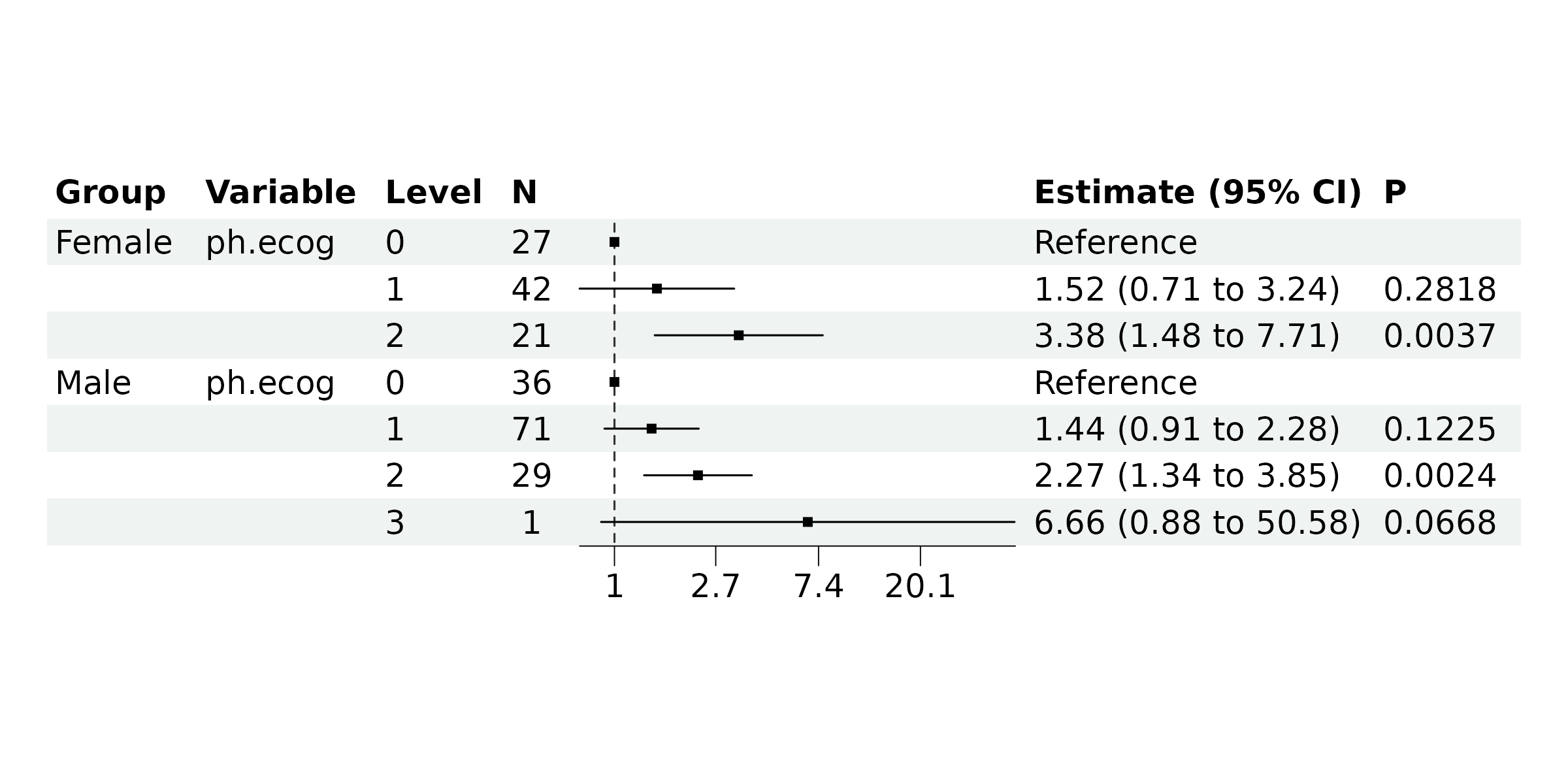
)Construct grouped batch survival models to determine if the variable
ph.ecog has different survival effects under different sex
groups.
mds <- br_pipeline(
data,
y = c("time", "status"),
x = "ph.ecog",
group_by = "sex",
method = "coxph"
)
#> exponentiate estimates of model(s) constructed from coxph method
#> at defaultWe can examine the constructed models.
br_get_models(mds)
#> $Female_ph.ecog
#> Call:
#> survival::coxph(formula = survival::Surv(time, status) ~ ph.ecog,
#> data = data)
#>
#> coef exp(coef) se(coef) z p
#> ph.ecog1 0.4162 1.5161 0.3867 1.076 0.28182
#> ph.ecog2 1.2190 3.3836 0.4204 2.900 0.00374
#> ph.ecog3 NA NA 0.0000 NA NA
#>
#> Likelihood ratio test=9.23 on 2 df, p=0.009894
#> n= 90, number of events= 53
#>
#> $Male_ph.ecog
#> Call:
#> survival::coxph(formula = survival::Surv(time, status) ~ ph.ecog,
#> data = data)
#>
#> coef exp(coef) se(coef) z p
#> ph.ecog1 0.3641 1.4393 0.2358 1.544 0.12251
#> ph.ecog2 0.8190 2.2682 0.2696 3.038 0.00238
#> ph.ecog3 1.8961 6.6596 1.0345 1.833 0.06682
#>
#> Likelihood ratio test=10.46 on 3 df, p=0.01503
#> n= 137, number of events= 111
#> (1 observation deleted due to missingness)
#>
#> $All_ph.ecog
#> Call:
#> survival::coxph(formula = survival::Surv(time, status) ~ ph.ecog,
#> data = data)
#>
#> coef exp(coef) se(coef) z p
#> ph.ecog1 0.3688 1.4461 0.1987 1.857 0.0634
#> ph.ecog2 0.9164 2.5002 0.2245 4.081 4.48e-05
#> ph.ecog3 2.2080 9.0973 1.0258 2.152 0.0314
#>
#> Likelihood ratio test=18.44 on 3 df, p=0.0003561
#> n= 227, number of events= 164
#> (1 observation deleted due to missingness)Now, display the results using a forest plot.
br_show_forest(mds)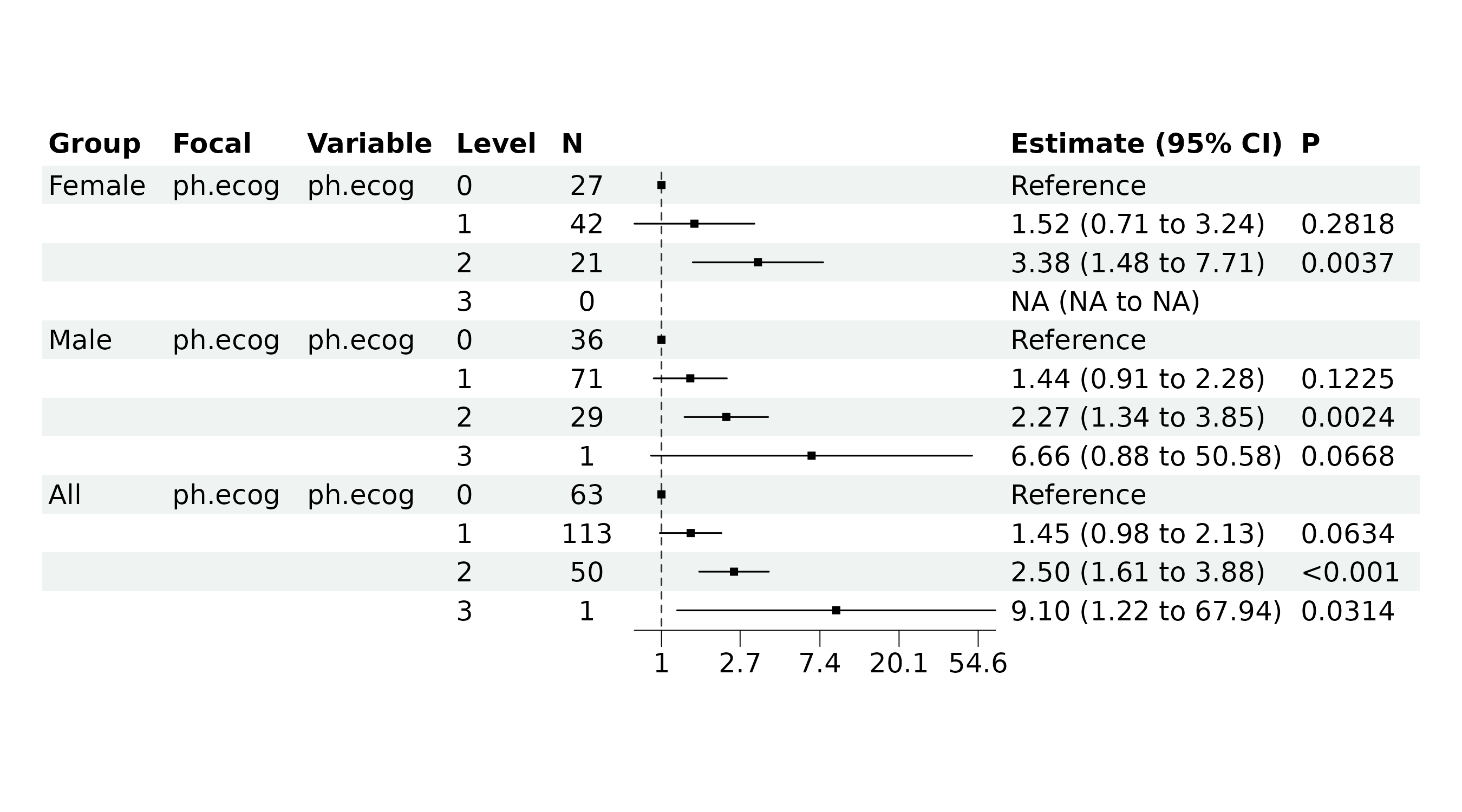
We can optimize the plot for better visualization, for example, by
removing the second column of the table and eliminating the row with
NA results.
br_show_forest(
mds,
drop = 2,
subset = !(Group_variable == "Female" & variable == "ph.ecog" & label == 3)
)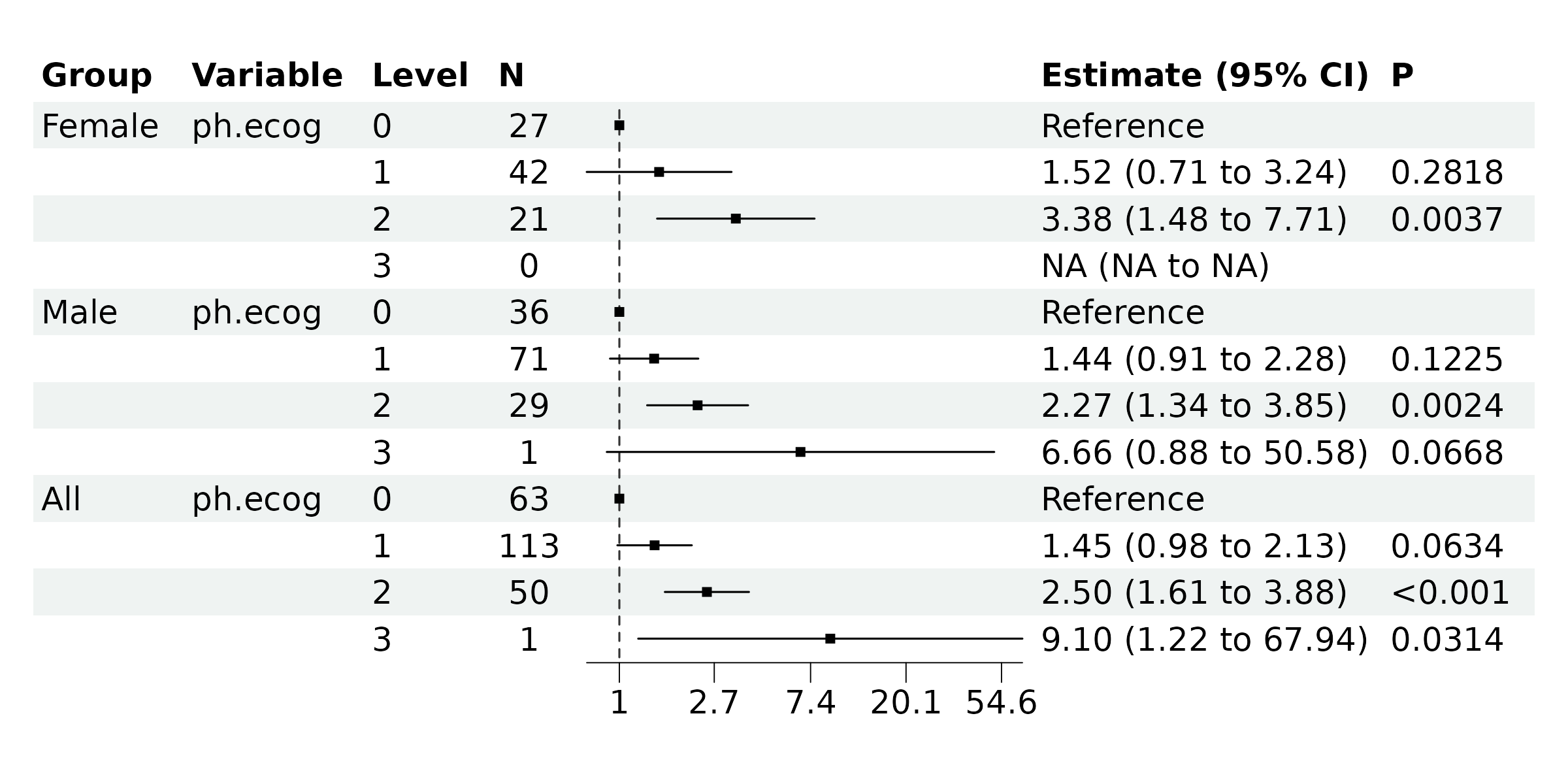
To subset the data rows, we can input an R expression using variables
from br_get_results(mds). For example, we can use
Group_variable == "Female" & variable == "ph.ecog" & label == 3
to locate the row we want to remove, and then use !() to
select the negated rows.
If drop All group is necessary, update the
subset with:
br_show_forest(
mds,
drop = 2,
subset = !((Group_variable == "Female" & variable == "ph.ecog" & label == 3) |
(Group_variable == "All"))
)